Since we have the user's timezone in the DB, we should use it to display the dates in the user's time.
Here's our plan:
Let's get started!
We'll start by creating a new Middleware that will set the timezone for the user. We'll call it SetTimezone and it will look like this:
app/Http/Middleware/SetTimezoneMiddleware.php
use Carbon\Carbon;use Closure;use DateTimeZone;use Illuminate\Http\Request; class SetTimezoneMiddleware{ public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next) { if (auth()->check()) { // This sets the default timezone for Carbon and PHP to the users timezone date_default_timezone_set(auth()->user()->timezone); // Here we are using php-intl extension to get users locale (at least trying to guess it!) $locale = new DateTimeZone(auth()->user()->timezone); $localeCode = $locale->getLocation()['country_code'] ?? 'en_US'; // Making sure Carbon knows which locale we will work with Carbon::setLocale($localeCode); } return $next($request); }}We'll also need to register this Middleware in our Kernel.php file:
app/Http/Kernel.php
// ... protected $middlewareAliases = [ // ... 'setTimezone' => \App\Http\Middleware\SetTimezoneMiddleware::class, ];And finally, we'll add it to our authenticated Routes:
routes/web.php
// ... Route::get('/dashboard', function () { return view('dashboard');})->middleware(['auth', 'verified'])->name('dashboard'); })->middleware(['auth', 'verified', 'setTimezone'])->name('dashboard'); Route::middleware(['auth', 'setTimezone'])->group(function () { Route::get('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'edit'])->name('profile.edit'); Route::patch('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'update'])->name('profile.update'); Route::delete('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'destroy'])->name('profile.destroy'); Route::resource('booking', BookingController::class);}); // ...The next step is to write Helpers that will convert the date to the user's timezone and back to UTC. For this, we'll use a Helpers file, which we need to register in our composer.json file:
composer.json
{ "autoload": { "psr-4": { "App\\": "app/", "Database\\Factories\\": "database/factories/", "Database\\Seeders\\": "database/seeders/" }, "files": [ "app/Helpers/worksWithDates.php" ] }}And create a Helper file:
app/Helpers/worksWithDates.php
use App\Models\User;use Carbon\Carbon; if (!function_exists('toUserDate')) { function toUserDate(string|Carbon $date, ?User $user = null, string $timezone = 'UTC'): string { if ($user) { $timezone = $user->timezone; } if (is_string($date)) { return Carbon::parse($date, 'UTC')->setTimezone($timezone)->isoFormat('L'); } return $date->setTimezone($timezone)->isoFormat('L'); }} if (!function_exists('toUserTime')) { function toUserTime(string|Carbon $date, ?User $user = null, string $timezone = 'UTC'): string { if ($user) { $timezone = $user->timezone; } if (is_string($date)) { return Carbon::parse($date, 'UTC')->setTimezone($timezone)->isoFormat('LT'); } return $date->setTimezone($timezone)->isoFormat('LT'); }} if (!function_exists('toUserDateTime')) { function toUserDateTime(string|Carbon $date, ?User $user = null, string $timezone = 'UTC'): string { if ($user) { $timezone = $user->timezone; } if (is_string($date)) { return Carbon::parse($date, 'UTC')->setTimezone($timezone)->isoFormat('L LT'); } return $date->setTimezone($timezone)->isoFormat('L LT'); }} if (!function_exists('fromUserDate')) { function fromUserDate(string|Carbon $date, ?User $user = null, string $timezone = null): string { if ($user) { $timezone = $user->timezone; } if (is_string($date)) { return Carbon::parse($date, $timezone)->setTimezone('UTC')->toDateString(); } return $date->setTimezone('UTC')->toDateTimeString(); }} if (!function_exists('fromUserTime')) { function fromUserTime(string|Carbon $date, ?User $user = null, string $timezone = null): string { if ($user) { $timezone = $user->timezone; } if (is_string($date)) { return Carbon::parse($date, $timezone)->setTimezone('UTC')->toTimeString(); } return $date->setTimezone('UTC')->toDateTimeString(); }} if (!function_exists('fromUserDateTime')) { function fromUserDateTime(string|Carbon $date, ?User $user = null, string $timezone = null): string { if ($user) { $timezone = $user->timezone; } if (is_string($date)) { return Carbon::parse($date, $timezone)->setTimezone('UTC')->toDateTimeString(); } return $date->setTimezone('UTC')->toDateTimeString(); }}This will allow us to use these functions anywhere in our code - from Controllers to Views.
But before we do that, let's make sure that we have tests for this!
php artisan make:test TimeConversionTest --unittests/Unit/TimeConversionTest.php
use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase; class TimeConversionTest extends TestCase{ public function test_correctly_transforms_utc_to_any_date(): void { $this->assertEquals('01/01/2023', toUserDate('2023-01-01')); $this->assertEquals('12/31/2022', toUserDate('2023-01-01', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('01/01/2023', toUserDate('2023-01-01', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // DST tests $this->assertEquals('07/01/2021', toUserDate('2021-07-01')); $this->assertEquals('06/30/2021', toUserDate('2021-07-01', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('07/01/2021', toUserDate('2021-07-01', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge-cases that we encounter } public function test_correctly_transforms_utc_to_any_time(): void { $this->assertEquals('12:00 AM', toUserTime('00:00:00')); $this->assertEquals('8:00 PM', toUserTime('00:00:00', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('1:00 AM', toUserTime('00:00:00', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge-cases that we encounter } public function test_correctly_transforms_utc_to_any_date_time(): void { $this->assertEquals('01/01/2023 12:00 AM', toUserDateTime('2023-01-01 00:00:00')); $this->assertEquals('12/31/2022 7:00 PM', toUserDateTime('2023-01-01 00:00:00', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('01/01/2023 12:00 AM', toUserDateTime('2023-01-01 00:00:00', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // DST tests $this->assertEquals('07/01/2021 12:00 AM', toUserDateTime('2021-07-01 00:00:00')); $this->assertEquals('06/30/2021 8:00 PM', toUserDateTime('2021-07-01 00:00:00', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('07/01/2021 1:00 AM', toUserDateTime('2021-07-01 00:00:00', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge-cases that we encounter } public function test_correctly_transforms_user_date_to_utc(): void { $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01', fromUserDate('01/01/2023')); $this->assertEquals('2022-12-31', fromUserDate('12/31/2022', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01', fromUserDate('01/01/2023', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // DST tests $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01', fromUserDate('07/01/2021')); $this->assertEquals('2021-06-30', fromUserDate('06/30/2021', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('2021-06-30', fromUserDate('07/01/2021', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge-cases that we encounter } public function test_correctly_transforms_users_time_to_utc(): void { $this->assertEquals('00:00:00', fromUserTime('12:00 AM')); $this->assertEquals('00:00:00', fromUserTime('8:00 PM', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('00:00:00', fromUserTime('1:00 AM', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge-cases that we encounter } public function test_correctly_transforms_user_date_time_to_utc(): void { $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('01/01/2023 12:00 AM')); $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('12/31/2022 7:00 PM', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01 01:00:00', fromUserDateTime('01/01/2023 1:00 AM', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // DST tests $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('07/01/2021 12:00 AM')); $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('06/30/2021 8:00 PM', timezone: 'America/New_York')); $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('07/01/2021 1:00 AM', timezone: 'Europe/London')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge-cases that we encounter } public function test_correctly_transforms_user_date_time_from_settings_to_utc(): void { $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('01/01/2023 12:00 AM')); date_default_timezone_set('America/New_York'); $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('12/31/2022 7:00 PM')); date_default_timezone_set('Europe/London'); $this->assertEquals('2023-01-01 01:00:00', fromUserDateTime('01/01/2023 1:00 AM')); // DST tests date_default_timezone_set('UTC'); $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('07/01/2021 12:00 AM')); date_default_timezone_set('America/New_York'); $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('06/30/2021 8:00 PM')); date_default_timezone_set('Europe/London'); $this->assertEquals('2021-07-01 00:00:00', fromUserDateTime('07/01/2021 1:00 AM')); // This can be expanded to include more tests and edge cases that we encounter }}Now we are ready to use these functions in our code.
Let's start with the Controller, to make sure we store the data correctly:
app/Http/Controllers/BookingController.php
// ...public function store(StoreBookingRequest $request): RedirectResponse{ $request->user()->bookings()->create([ 'start' => $request->validated('start'), 'start' => fromUserDateTime($request->validated('start')), 'end' => $request->validated('end'), 'end' => fromUserDateTime($request->validated('end')), ]); return redirect()->route('booking.index');} // ... public function update(UpdateBookingRequest $request, Booking $booking): RedirectResponse{ $booking->update([ 'start' => $request->validated('start'), 'start' => fromUserDateTime($request->validated('start')), 'end' => $request->validated('end'), 'end' => fromUserDateTime($request->validated('end')), ]); return redirect()->route('booking.index');}// ...As you can see, we are taking the user's date and converting it to the UTC format using the fromUserDateTime() function. This ensures that all the dates/times we are storing are in UTC format and not in any other format.
For example, creating a booking with the following data in the NY timezone:
It will save the following data in the database:

The last step is to make sure we display the dates/times in the correct format to the user. We can do that by using the toUserDateTime() function:
resources/views/booking/index.blade.php
@foreach($bookings as $booking) <tr> <td class="border px-4 py-2">{{ $booking->id }}</td> <td class="border px-4 py-2">{{ $booking->user->name }}</td> <td class="border px-4 py-2">{{ $booking->start }}</td> <td class="border px-4 py-2">{{ toUserDateTime($booking->start, auth()->user()) }}</td> <td class="border px-4 py-2">{{ $booking->end }}</td> <td class="border px-4 py-2">{{ toUserDateTime($booking->end, auth()->user()) }}</td> <td class="border px-4 py-2 text-center"> // ... </td> </tr>@endforeachSince it accepts a second parameter, we are passing the currently logged-in user. But we also can pass any other user, which will display the date/time in the correct format in that user's timezone.
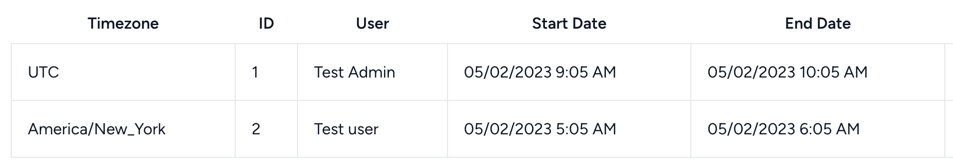
You will see there's a difference in what is being displayed on the UI (in this case, I'm displaying by user timezone):

While our database has exactly the same start/end dates:

That's because they are in different timezones, and we are converting UTC time to the required timezone.
The same example, just with a display in the same timezone for all users, would look like this:

Code in Repository