So now that we have some plan let's start implementing it. We will start by installing Laravel Breeze starter kit for quick authentication scaffolding and a simple layout. Then, we will create the first CRUD for companies.
So first, we will install Breeze.
composer require laravel/breeze --devphp artisan breeze:install bladeDuring the planning phase, we added a Role table and a role_id column to the User table. Because of this, if you try to register, you will get an error:
SQLSTATE[HY000]: General error: 1364 Field 'role_id' doesn't have a default valueSo, we need to add the default roles and assign a role when a user registers.
For adding roles, we will create a Seeder.
php artisan make:seeder RoleSeederdatabase/seeders/RoleSeeder.php:
use App\Models\Role; class RoleSeeder extends Seeder{ public function run(): void { Role::create(['name' => 'administrator']); Role::create(['name' => 'company owner']); Role::create(['name' => 'customer']); Role::create(['name' => 'guide']); }}And add this Seeder to the DatabaseSeeder.
database/seeders/DatabaseSeeder.php:
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder{ public function run(): void { $this->call([ RoleSeeder::class, ]); }}When the user registers, we need to assign a role. We could add the ID of the customer role in the RegisteredUserController of Laravel Breeze. But if a new developer would join this project sometime in the future, he wouldn't know what that number means. For this, we will use the PHP Enums feature.
Enum can be created using an Artisan command make:enum.
php artisan make:enum Enums\Role --intInside app/Enums/Role.php, we need to add all the roles; their value will be the ID.
app/Enums/Role.php:
enum Role: int{ case ADMINISTRATOR = 1; case COMPANY_OWNER = 2; case CUSTOMER = 3; case GUIDE = 4;}So now, we can use Role Enum where we need it.
app/Http/Controllers/Auth/RegisteredUserController.php:
use App\Enums\Role; class RegisteredUserController extends Controller{ public function store(Request $request): RedirectResponse { // ... $user = User::create([ 'name' => $request->name, 'email' => $request->email, 'password' => Hash::make($request->password), 'role_id' => Role::CUSTOMER->value, ]); // ... }}Now we can register, great!
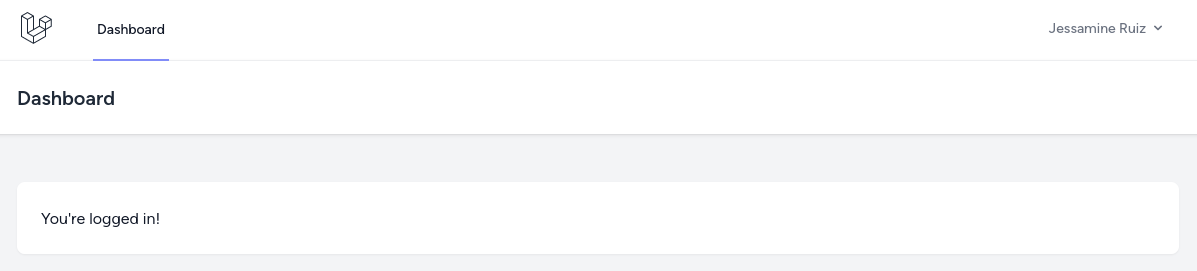
Ok, now we can move to the actual functionality, and looking at the plan, we'll start with managing companies.
Next, we can create the companies CRUD. For now, it will be available to everyone, and in the next lesson, we will restrict this functionality to administrators only.
In general, my approach: first focus on making the feature itself work and then add more validation and restrictions.
So, first, we need a Controller and a Route.
php artisan make:controller CompanyControllerroutes/web.php:
use App\Http\Controllers\CompanyController; Route::middleware('auth')->group(function () { Route::get('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'edit'])->name('profile.edit'); // ... Route::resource('companies', CompanyController::class); });And let's add a navigation link in the menu, just next to the dashboard. We will copy-paste the existing Laravel Breeze x-nav-link component for that.
resources/views/layouts/navigation.blade.php:
// ...<!-- Navigation Links --><div class="hidden space-x-8 sm:-my-px sm:ml-10 sm:flex"> <x-nav-link :href="route('dashboard')" :active="request()->routeIs('dashboard')"> {{ __('Dashboard') }} </x-nav-link> <x-nav-link :href="route('companies.index')" :active="request()->routeIs('companies.index')"> {{ __('Companies') }} </x-nav-link> </div>// ...Next, in the Controller, we need to get all the companies and show them.
We will save all Blade files related to companies in the resources/views/companies directory: it's a common practice to have files like this, often corresponding to the Controller methods:
resources/views/[feature-name]/index.blade.php
resources/views/[feature-name]/create.blade.php
resources/views/[feature-name]/edit.blade.php
app/Http/Controllers/CompanyController.php
use App\Models\Company;use Illuminate\View\View; class CompanyController extends Controller{ public function index(): View { $companies = Company::all(); return view('companies.index', compact('companies')); }}And here's the Blade View file to show all the companies.
resources/views/companies/index.blade.php:
<x-app-layout> <x-slot name="header"> <h2 class="text-xl font-semibold leading-tight text-gray-800"> {{ __('Companies') }} </h2> </x-slot> <div class="py-12"> <div class="mx-auto max-w-7xl sm:px-6 lg:px-8"> <div class="overflow-hidden bg-white shadow-sm sm:rounded-lg"> <div class="overflow-hidden overflow-x-auto border-b border-gray-200 bg-white p-6"> <a href="{{ route('companies.create') }}" class="mb-4 inline-flex items-center rounded-md border border-gray-300 bg-white px-4 py-2 text-xs font-semibold uppercase tracking-widest text-gray-700 shadow-sm transition duration-150 ease-in-out hover:bg-gray-50 focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-indigo-500 focus:ring-offset-2 disabled:opacity-25"> Create </a> <div class="min-w-full align-middle"> <table class="min-w-full border divide-y divide-gray-200"> <thead> <tr> <th class="bg-gray-50 px-6 py-3 text-left"> <span class="text-xs font-medium uppercase leading-4 tracking-wider text-gray-500">Name</span> </th> <th class="w-56 bg-gray-50 px-6 py-3 text-left"> </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody class="bg-white divide-y divide-gray-200 divide-solid"> @foreach($companies as $company) <tr class="bg-white"> <td class="px-6 py-4 text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900 whitespace-no-wrap"> {{ $company->name }} </td> <td class="px-6 py-4 text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900 whitespace-no-wrap"> <a href="{{ route('companies.edit', $company) }}" class="inline-flex items-center rounded-md border border-gray-300 bg-white px-4 py-2 text-xs font-semibold uppercase tracking-widest text-gray-700 shadow-sm transition duration-150 ease-in-out hover:bg-gray-50 focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-indigo-500 focus:ring-offset-2 disabled:opacity-25"> Edit </a> <form action="{{ route('companies.destroy', $company) }}" method="POST" onsubmit="return confirm('Are you sure?')" style="display: inline-block;"> @csrf @method('DELETE') <x-danger-button> Delete </x-danger-button> </form> </td> </tr> @endforeach </tbody> </table> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div></x-app-layout>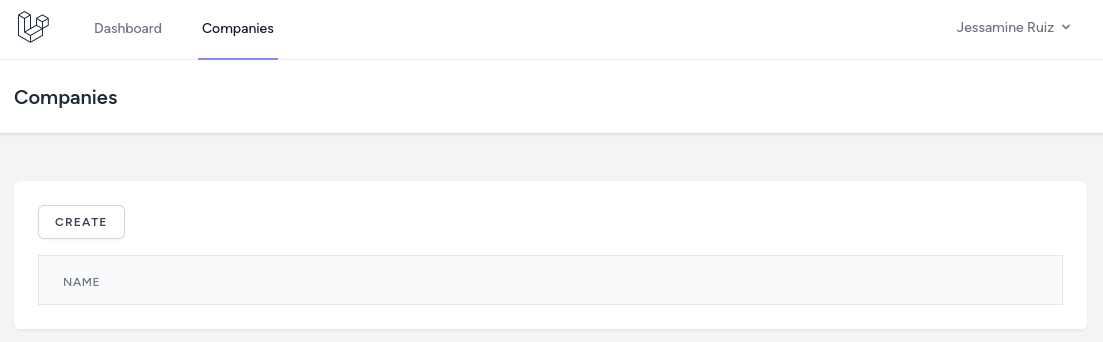
Now that we can show companies, let's add the create and edit forms.
We will use Form Requests for the validation. Let's generate them immediately so we can use them in the Controller.
php artisan make:request StoreCompanyRequestphp artisan make:request UpdateCompanyRequestRules in the form request for both save and update are the same.
app/Http/Requests/StoreCompanyRequest.php:
class StoreCompanyRequest extends FormRequest{ public function authorize(): bool { return true; } public function rules(): array { return [ 'name' => ['required', 'string'], ]; }}app/Http/Requests/UpdateCompanyRequest.php:
class UpdateCompanyRequest extends FormRequest{ public function authorize(): bool { return true; } public function rules(): array { return [ 'name' => ['required', 'string'], ]; }}The Controller code for creating and updating:
app/Http/Controllers/CompanyController.php:
use Illuminate\Http\RedirectResponse;use App\Http\Requests\StoreCompanyRequest;use App\Http\Requests\UpdateCompanyRequest; class CompanyController extends Controller{ // ... public function create(): View { return view('companies.create'); } public function store(StoreCompanyRequest $request): RedirectResponse { Company::create($request->validated()); return to_route('companies.index'); } public function edit(Company $company) { return view('companies.edit', compact('company')); } public function update(UpdateCompanyRequest $request, Company $company): RedirectResponse { $company->update($request->validated()); return to_route('companies.index'); }}And here are both create and edit forms.
resources/views/companies/create.blade.php:
<x-app-layout> <x-slot name="header"> <h2 class="text-xl font-semibold leading-tight text-gray-800"> {{ __('Create Company') }} </h2> </x-slot> <div class="py-12"> <div class="mx-auto max-w-7xl sm:px-6 lg:px-8"> <div class="overflow-hidden bg-white shadow-sm sm:rounded-lg"> <div class="overflow-hidden overflow-x-auto border-b border-gray-200 bg-white p-6"> <form action="{{ route('companies.store') }}" method="POST"> @csrf <div> <x-input-label for="name" value="Name" /> <x-text-input id="name" name="name" value="{{ old('name') }}" type="text" class="block mt-1 w-full" /> <x-input-error :messages="$errors->get('name')" class="mt-2" /> </div> <div class="mt-4"> <x-primary-button> Save </x-primary-button> </div> </form> </div> </div> </div> </div></x-app-layout>resources/views/companies/edit.blade.php:
<x-app-layout> <x-slot name="header"> <h2 class="text-xl font-semibold leading-tight text-gray-800"> {{ __('Edit Company') }} </h2> </x-slot> <div class="py-12"> <div class="mx-auto max-w-7xl sm:px-6 lg:px-8"> <div class="overflow-hidden bg-white shadow-sm sm:rounded-lg"> <div class="overflow-hidden overflow-x-auto border-b border-gray-200 bg-white p-6"> <form action="{{ route('companies.update', $company) }}" method="POST"> @csrf @method('PUT') <div> <x-input-label for="name" value="Name" /> <x-text-input id="name" name="name" value="{{ old('name', $company->name) }}" type="text" class="block mt-1 w-full" /> <x-input-error :messages="$errors->get('name')" class="mt-2" /> </div> <div class="mt-4"> <x-primary-button> Save </x-primary-button> </div> </form> </div> </div> </div> </div></x-app-layout>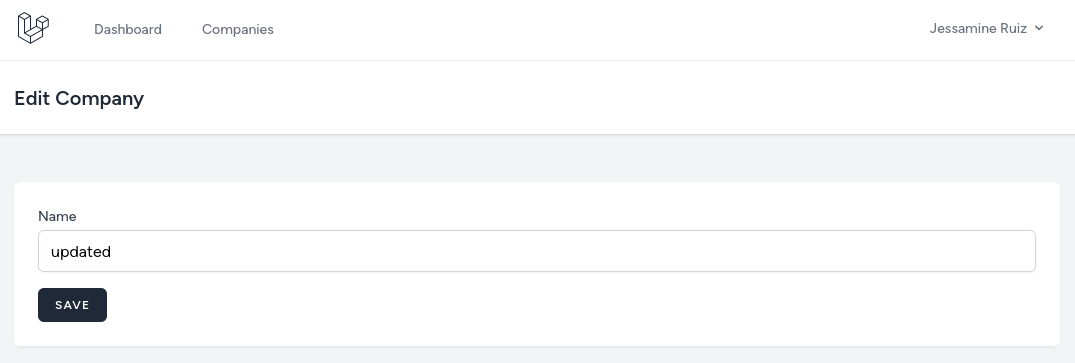
Now we need to implement the delete method. Not sure if you noticed, but I've already added the Delete button before, when creating the list page.
All that's left is to add a method to the Controller.
app/Http/Controllers/CompanyController.php:
class CompanyController extends Controller{ // ... public function destroy(Company $company) { $company->delete(); return to_route('companies.index'); }}That's it! We have fully working companies CRUD. Let's move on to the next lesson.