Now, let's start writing tests for a simple but real project that would list the products.
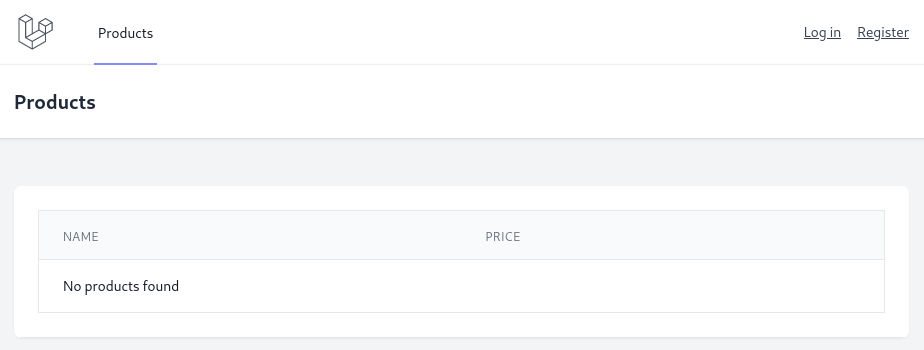
First, we will make a simple page listing the products. For the frontend, we will be using Laravel Breeze. So first, the Model and Migration.
database/migrations/xxx_create_products_table.php:
public function up(): void{ Schema::create('products', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->integer('price'); $table->timestamps(); });}app/Models/Product.php:
class Product extends Model{ protected $fillable = [ 'name', 'price', ];}Next, the Controller, View, and Route.
app/Http/Controllers/ProductController.php:
use App\Models\Product;use Illuminate\Contracts\View\View; class ProductController extends Controller{ public function index(): View { $products = Product::all(); return view('products.index', compact('products')); }}resources/views/products/index.blade.php:
<x-app-layout> <x-slot name="header"> <h2 class="font-semibold text-xl text-gray-800 leading-tight"> {{ __('Products') }} </h2> </x-slot> <div class="py-12"> <div class="max-w-7xl mx-auto sm:px-6 lg:px-8"> <div class="bg-white overflow-hidden shadow-sm sm:rounded-lg"> <div class="overflow-hidden overflow-x-auto p-6 bg-white border-b border-gray-200"> <div class="min-w-full align-middle"> <table class="min-w-full divide-y divide-gray-200 border"> <thead> <tr> <th class="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 text-left"> <span class="text-xs leading-4 font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase tracking-wider">Name</span> </th> <th class="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 text-left"> <span class="text-xs leading-4 font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase tracking-wider">Price</span> </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody class="bg-white divide-y divide-gray-200 divide-solid"> @forelse($products as $product) <tr class="bg-white"> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ $product->name }} </td> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> ${{ number_format($product->price, 2) }} </td> </tr> @empty <tr class="bg-white"> <td colspan="2" class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ __('No products found') }} </td> </tr> @endforelse </tbody> </table> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div></x-app-layout>routes/web.php:
use App\Http\Controllers\ProductController; Route::get('/', function () { return view('home');})->name('home'); Route::resource('products', ProductController::class); // ...Notice: we are using Resource for Route because later, we will add other methods like
create(),store(), etc.
After visiting /products, we should see an empty table.

Now, let's write tests for this page.
For the first tests, we will check two scenarios:
No products found when there are no recordsReminder: We will use Pest PHP testing framework in this course. At the end of the lesson, we will see how the same could be achieved using PHPUnit.
We can create a new test class using an artisan command. It will generate a feature test.
php artisan make:test ProductsTestIn this test, we need to get the /products URL and, from the response, assert if we see the No products found text. The test's name will be homepage contains empty table so that it will be clear what it tests.
tests/Feature/ProductsTest.php:
use function Pest\Laravel\get; test('homepage contains empty table', function () { get('/products') ->assertStatus(200) ->assertSee(__('No products found'));});Instead of using typical $this->get() syntax we used the get() function from the pestphp/pest-plugin-laravel plugin.
If we run the tests, we will see this new test passed successfully.
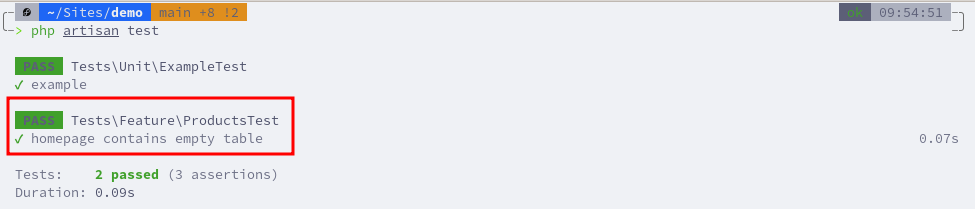
Let's add another test to assert that the No products found text isn't rendered when the products DB is not empty. Instead of assertSee(), the opposite assertDontSee() method is used.
For now, we will create the product manually inside the test, and later, we will see how to do it automatically in a separate testing database.
tests/Feature/ProductsTest.php:
use App\Models\Product;use function Pest\Laravel\get; test('homepage contains empty table', function () { get('/products') ->assertStatus(200) ->assertSee(__('No products found'));}); test('homepage contains non empty table', function () { Product::create([ 'name' => 'Product 1', 'price' => 123, ]); get('/products') ->assertStatus(200) ->assertDontSee(__('No products found'));}); Run the tests.
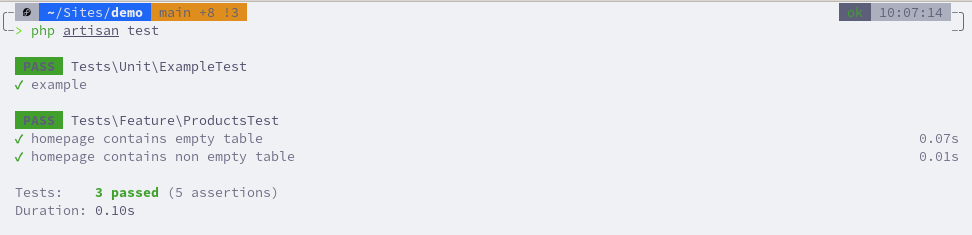
So, this is how you write tests to see if some text is/isn't present on the page.
To create a new PHPUnit test class, the --phpunit parameter must be added to the make:test artisan command.
php artisan make:test ProductsTest --phpunittests/Feature/ProductsTest.php:
class ProductsTest extends TestCase{ public function test_homepage_contains_empty_table(): void { $response = $this->get('/products'); $response->assertStatus(200); $response->assertSee(__('No products found')); }}The second test to assert that the No products found text isn't rendered.
tests/Feature/ProductsTest.php:
use App\Models\Product; class ProductsTest extends TestCase{ public function test_homepage_contains_empty_table(): void { $response = $this->get('/products'); $response->assertStatus(200); $response->assertSee(__('No products found')); } public function test_homepage_contains_non_empty_table(): void { Product::create([ 'name' => 'Product 1', 'price' => 123, ]); $response = $this->get('/products'); $response->assertStatus(200); $response->assertDontSee(__('No products found')); } }Run the tests.

So, we have covered another simple example: simulated both cases in the products table when it is and isn't empty.