.png-674b523429100.jpg)
In this tutorial, we will create a simple search from three Models and will use Laravel Collections to combine them into one collection to show results in the front-end.
Also, we will make the table row background color to be based on the Model. And finally, we will add pagination to the Collection to show results with the pagination links.
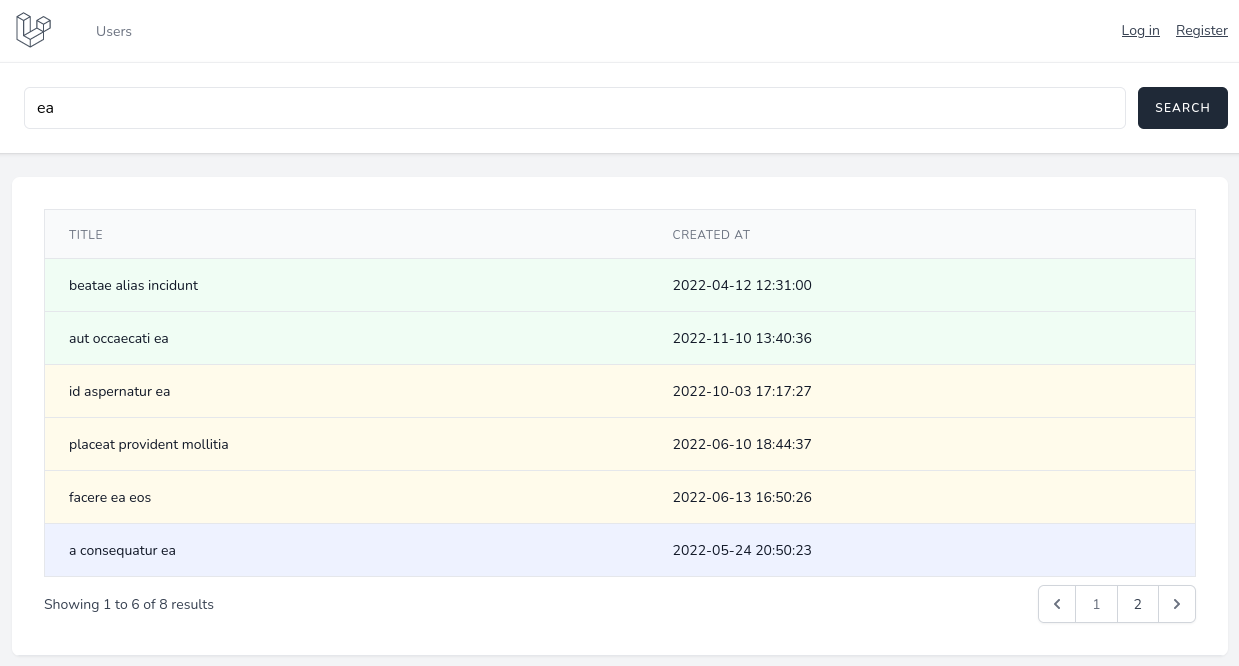
In the end, we will have a similar result to this:
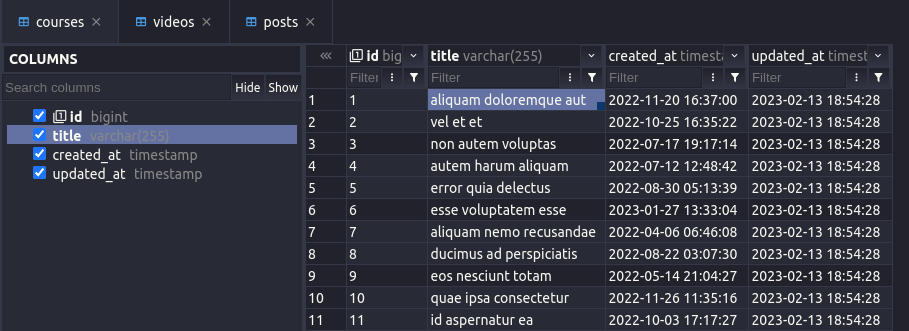
The structure of the database here is very simple. We have three models Post, Video, and Course, and each has a title column. Seeded data would look similar to this:
Now for the controller where the search happens. In the search form, input has the name of query and because the form uses the GET method, after submitting the form we are getting to URL similar to /search?query=. In the controller, we can get the query parameter using Request. Using all of this, we can search this:
use Illuminate\Http\Request; class SearchController extends Controller{ public function __invoke(Request $request) { $posts = Post::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $courses = Course::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $videos = Video::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); }}Now that we have all results, we can add them to one collection. To do that, we first need to create a new collection and use the push() method to add items to the end of the collection.
class SearchController extends Controller{ public function __invoke(Request $request) { $posts = Post::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $courses = Course::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $videos = Video::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $results = collect(); $results->push($posts, $courses, $videos); }}After this, $results will give a similar result to this:
Illuminate\Support\Collection {#302 ▼ // app/Http/Controllers/SearchController.php:21 #items: array:3 [▼ 0 => Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection {#1043 ▼ #items: array:2 [▼ 0 => App\Models\Post {#1255 ▶} 1 => App\Models\Post {#1256 ▶} ] #escapeWhenCastingToString: false } 1 => Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection {#1257 ▼ #items: array:3 [▼ 0 => App\Models\Course {#1260 ▶} 1 => App\Models\Course {#1261 ▶} 2 => App\Models\Course {#1262 ▶} ] #escapeWhenCastingToString: false } 2 => Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection {#1109 ▼ #items: array:3 [▼ 0 => App\Models\Video {#1265 ▶} 1 => App\Models\Video {#1266 ▶} 2 => App\Models\Video {#1267 ▶} ] #escapeWhenCastingToString: false } ] #escapeWhenCastingToString: false}But in this structure, we cannot iterate through all data easily. Now, we need to make this multi-dimensional collection into a single dimension. For that, we just need to use the flatten() method and return the result to the view.
class SearchController extends Controller{ public function __invoke(Request $request) { $posts = Post::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $courses = Course::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $videos = Video::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $results = collect(); $results->push($posts, $courses, $videos); return view('search', ['results' => $results->flatten()]); }}Now, we have a Collection in a nice easily iterate-able structure.
Illuminate\Support\Collection {#308 ▼ // app/Http/Controllers/SearchController.php:21 #items: array:8 [▼ 0 => App\Models\Post {#1255 ▶} 1 => App\Models\Post {#1256 ▶} 2 => App\Models\Course {#1260 ▶} 3 => App\Models\Course {#1261 ▶} 4 => App\Models\Course {#1262 ▶} 5 => App\Models\Video {#1265 ▶} 6 => App\Models\Video {#1266 ▶} 7 => App\Models\Video {#1267 ▶} ] #escapeWhenCastingToString: false}All that's left is to show results. We just can use @forelse to go through all results, and @empty to write if no results were found. And using instanceof we can change the background of the table row for a specific result.
<tbody class="bg-white divide-y divide-gray-200 divide-solid"> @forelse($results as $result) <tr @class([ 'bg-green-50' => $result instanceof App\Models\Post, 'bg-indigo-50' => $result instanceof App\Models\Video, 'bg-amber-50' => $result instanceof App\Models\Course, ])> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ $result->title }} </td> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ $result->created_at }} </td> </tr> @empty No results found. @endforelse</tbody>Of course, you might have many results, and for that, you would want to paginate results. But collections don't have an out-of-box method to paginate. To do that we have two ways. One is to use package spatie/laravel-collection-macros and another is to create macro yourself. Both ways code will be the same. To add macros you typically would add them in the boot() of a service provider.
use Illuminate\Support\Collection;use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;use Illuminate\Pagination\LengthAwarePaginator; class AppServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider{ // public function boot(): void { Collection::macro('paginate', function ($perPage = 15, $total = null, $page = null, $pageName = 'page') { $page = $page ?: LengthAwarePaginator::resolveCurrentPage($pageName); return new LengthAwarePaginator( $this->forPage($page, $perPage), $total ?: $this->count(), $perPage, $page, [ 'path' => LengthAwarePaginator::resolveCurrentPath(), 'pageName' => $pageName, ] ); }); }}Now you can add the paginate() method to the $results.
class SearchController extends Controller{ public function __invoke(Request $request) { $posts = Post::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $courses = Course::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $videos = Video::where('title', 'like', '%' . $request->input('query') . '%')->get(); $results = collect(); $results->push($posts, $courses, $videos); return view('search', ['results' => $results->flatten()]); return view('search', ['results' => $results->flatten()->paginate()]); }}Don't forget, when adding links() to show pagination, to add withQueryString() so that when going through pages $query parameter would be appended.
{{ $results->withQueryString()->links() }}That's it for this tutorial. If you want to learn more about Collections and especially how to use them in chains with real-world examples, you can watch the video course Laravel Collections Chains: 15 Real Examples or read the text-form Premium Tutorial Laravel Collections: 15 Open-Source Examples of "Chained" Methods.