;-$table-integer('price');-(1).png-674b5213c077a.jpg)
For multi-currency projects, there's no single solution. In this tutorial, we'll take a look at different approaches to this problem: DB schema, currency rate calculation, and more.
We will compare three models for PHP/Laravel projects:
Let's go!
When attempting to find a solution for this - you might encounter a suggestion to use real-time currency exchange API. This approach looks into converting your base currency (like USD or EUR) to another currency based on a real-time exchange rate.
USD or EUR)GBP)Of course, there are many things that you need to save/modify in your database:
USD, EUR, GBP, etc.)GBP) in the database - Two simple columns should do it charged_currency and charged_amount.0.8) - Two simple columns should do it exchange_rate and exchange_rate_date.USD) - Two simple columns should do it original_currency and original_amount.Your migration might look something like this:
Schema::create('products', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->integer('price'); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('orders', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('user_id')->constrained(); $table->integer('original_price'); $table->string('original_currency'); $table->integer('charged_price'); $table->string('charged_currency'); $table->float('exchange_rate')->nullable(); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('order_products', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('order_id')->constrained(); $table->foreignId('product_id')->constrained(); $table->integer('original_price'); $table->string('original_currency'); $table->integer('charged_price'); $table->string('charged_currency'); $table->float('exchange_rate')->nullable(); $table->integer('quantity')->default(1); $table->timestamps();});Which would result in a database schema like this:
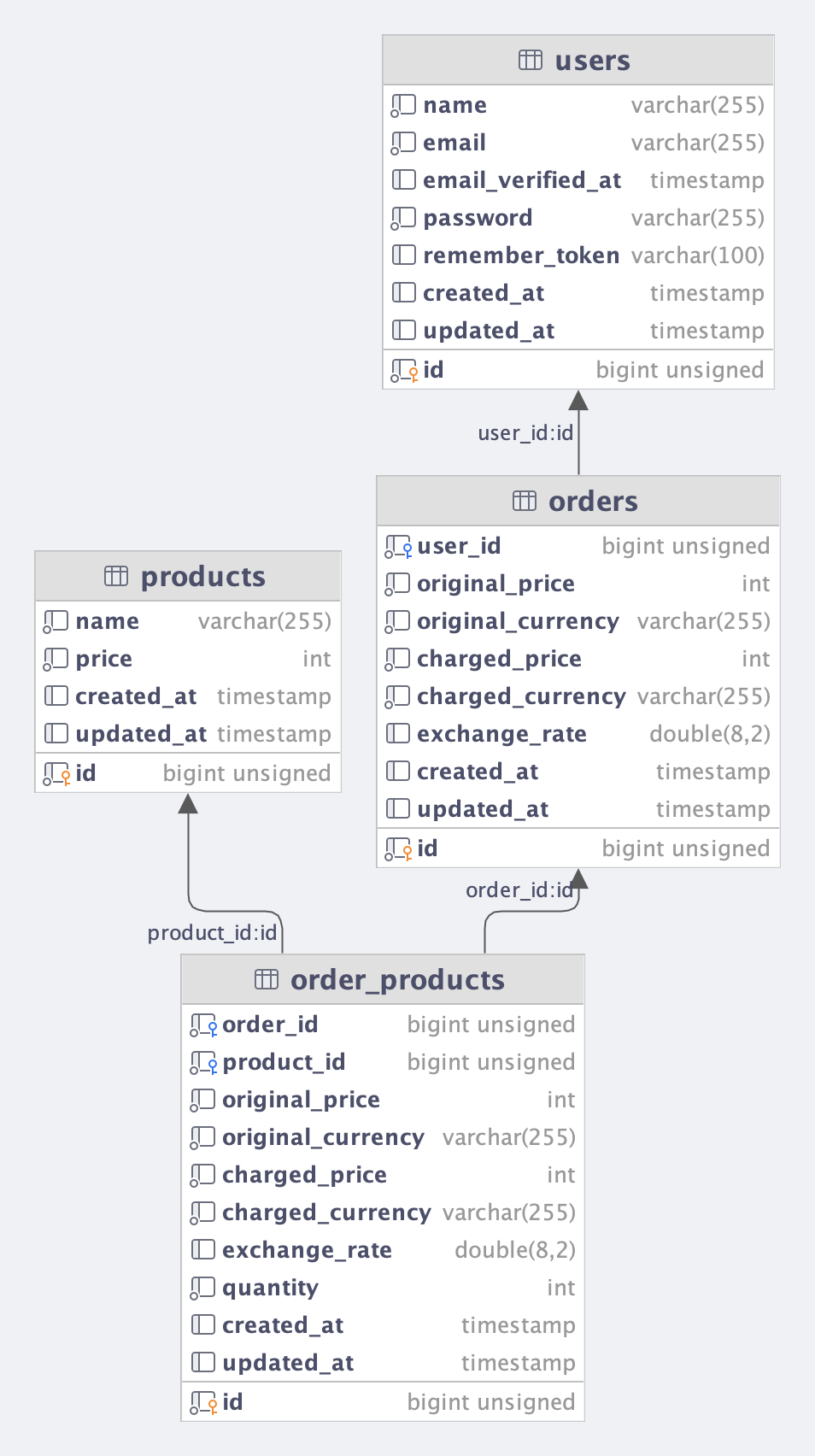
Pay attention to the saving of original currency and exchanged currency in both the orders table and the order_products table. This is key to generating reports quickly in your default currency but still having reference points to the exchanged currency.
original and charged currency) to have reported in a unified styleIn my opinion, this is not the best approach for this problem, but it's fast to implement and will give you a quick solution to this problem. If you're looking for a quick solution - this is the way to go. If you're looking for a more complex solution - you might want to take a look at the next approaches.
Referenced tutorial for this approach:
Another popular way to manage multi-currency in your applications is having a list of currencies and saving product prices in each currency. This approach gives you the ability to define prices as you see fit. For example, if you have a product that you want to sell for 100 USD and 80 EUR - you can do it.
This example can be found in Prestashop - a popular e-commerce platform. Let's take a look:
USD, EUR, GBP, etc.)US, UK, DE, etc.)currency_id attached to them100 in USD, 80 in EUR, etc.)Let's look at their database schema:
/* Currency specification */CREATE TABLE `PREFIX_currency` ( `id_currency` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment, `name` varchar(64) NOT NULL, /* Deprecated since 1.7.5.0. Use PREFIX_currency_lang.name instead. */ `iso_code` varchar(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `numeric_iso_code` varchar(3), `precision` int(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 6, `conversion_rate` decimal(13,6) NOT NULL, `deleted` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `active` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `unofficial` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `modified` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', PRIMARY KEY (`id_currency`), KEY `currency_iso_code` (`iso_code`)) ENGINE=ENGINE_TYPE DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATION; /* Country specific data */CREATE TABLE `PREFIX_country` ( `id_country` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment, `id_zone` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `id_currency` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', /* Currency */ `iso_code` varchar(3) NOT NULL, `call_prefix` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `active` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `contains_states` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `need_identification_number` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `need_zip_code` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `zip_code_format` varchar(12) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `display_tax_label` BOOLEAN NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id_country`), KEY `country_iso_code` (`iso_code`), KEY `country_` (`id_zone`)) ENGINE=ENGINE_TYPE DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATION; /* List of price reduction depending on given conditions */CREATE TABLE `PREFIX_specific_price` ( `id_specific_price` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `id_specific_price_rule` INT(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `id_cart` INT(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `id_product` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `id_shop` INT(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `id_shop_group` INT(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `id_currency` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, /* Currency */ `id_country` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, /* Country */ `id_group` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `id_customer` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `id_product_attribute` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `price` DECIMAL(20, 6) NOT NULL, `from_quantity` mediumint(8) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `reduction` DECIMAL(20, 6) NOT NULL, `reduction_tax` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1, `reduction_type` ENUM('amount', 'percentage') NOT NULL, `from` DATETIME NOT NULL, `to` DATETIME NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id_specific_price`), KEY ( `id_product`, `id_shop`, `id_currency`, `id_country`, `id_group`, `id_customer`, `from_quantity`, `from`, `to` ), KEY `from_quantity` (`from_quantity`), KEY (`id_specific_price_rule`), KEY (`id_cart`), KEY `id_product_attribute` (`id_product_attribute`), KEY `id_shop` (`id_shop`), KEY `id_customer` (`id_customer`), KEY `from` (`from`), KEY `to` (`to`), UNIQUE KEY `id_product_2` ( `id_product`, `id_product_attribute`, `id_customer`, `id_cart`, `from`, `to`, `id_shop`, `id_shop_group`, `id_currency`, `id_country`, `id_group`, `from_quantity`, `id_specific_price_rule` )) ENGINE=ENGINE_TYPE DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATION; /* List of orders */CREATE TABLE `PREFIX_orders` ( `id_order` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment, `reference` VARCHAR(9), `id_shop_group` INT(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `id_shop` INT(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `id_carrier` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `id_lang` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `id_customer` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `id_cart` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `id_currency` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, /* Currency */ `id_address_delivery` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `id_address_invoice` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `current_state` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL, `secure_key` varchar(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '-1', `payment` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `conversion_rate` decimal(13, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1, `module` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `recyclable` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `gift` tinyint(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `gift_message` text, `mobile_theme` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `total_discounts` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_discounts_tax_incl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_discounts_tax_excl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_paid` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_paid_tax_incl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_paid_tax_excl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_paid_real` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_products` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_products_wt` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_shipping` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_shipping_tax_incl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_shipping_tax_excl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `carrier_tax_rate` DECIMAL(10, 3) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_wrapping` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_wrapping_tax_incl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `total_wrapping_tax_excl` decimal(20, 6) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `round_mode` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '2', `round_type` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `invoice_number` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `delivery_number` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `invoice_date` datetime NOT NULL, `delivery_date` datetime NOT NULL, `valid` int(1) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `date_add` datetime NOT NULL, `date_upd` datetime NOT NULL, `note` text, PRIMARY KEY (`id_order`), KEY `reference` (`reference`), KEY `id_customer` (`id_customer`), KEY `id_cart` (`id_cart`), KEY `invoice_number` (`invoice_number`), KEY `id_carrier` (`id_carrier`), KEY `id_lang` (`id_lang`), KEY `id_currency` (`id_currency`), KEY `id_address_delivery` (`id_address_delivery`), KEY `id_address_invoice` (`id_address_invoice`), KEY `id_shop_group` (`id_shop_group`), KEY (`current_state`), KEY `id_shop` (`id_shop`), INDEX `date_add`(`date_add`)) ENGINE=ENGINE_TYPE DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATION;There's of course more to it but this is the base for it. All products can have per-currency price rules and those will be used everywhere in the system.
Our approach to building the multi-currency system is based on the previous principles while expanding them.
currencies table (id, iso_code, left_symbol, right_symbol)countries table (id, name, iso_code, currency_id)prices that will have different prices for different currencies (id, product_id, currency_id, price)currency_id column to display in which currency the order was madecurrency_id, and country_id columns to display in which currency the user wants to see the prices and to which country the user belongs toMigration Example
Schema::create('currencies', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->string('iso'); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('countries', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->string('iso'); $table->foreignId('currency_id')->constrained(); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('products', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('product_prices', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('product_id')->constrained(); $table->foreignId('currency_id')->constrained(); $table->integer('price'); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('orders', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('user_id')->constrained(); $table->foreignId('currency_id')->constrained(); $table->integer('sale_price'); // ... $table->timestamps();}); Schema::create('order_products', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('order_id')->constrained(); $table->foreignId('product_id')->constrained(); $table->foreignId('currency_id')->constrained(); $table->string('sale_price'); $table->integer('quantity')->default(1); $table->timestamps();}); Schema::table('users', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->foreignId('country_id')->nullable()->constrained(); $table->foreignId('currency_id')->nullable()->constrained();});And here's how it would look in our database:

This can be expanded with automatic exchange rates and other features.
With this approach we can:
As mentioned previously - there's no one-size-fits-all solution out there. Everyone has different needs. If your shop is small, or you are going to serve a small audience - direct exchange API might work. If you are looking into your own country and a few close countries to sell - you might want to use a simple pricing table with just prices per country. If you are looking to go international and want to implement things like PPP - you will have to go the full length and support multiple countries and their currencies separately.